Our research began with exploring the differences between IPF patients and healthy people and identified that the levels of HIF-1α, NOX4 and ROS in IPF patients are much higher than those in healthy people. The study results suggest that hypoxia as well as inflammation is a potential driver of IPF.
-
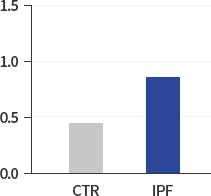
HIF-1α/β:ACTIN
-
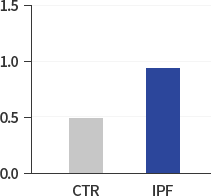
NOX4:GAPDH
(densitometric analysis) -
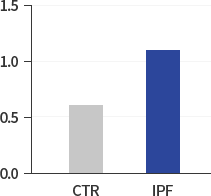
Superoxide O2-
(nMol/100.000Cells)
Hypoxia-induced HIF-1α was identified as a pivotal driver of IPF based on cellular study results below. The study suggests that due to IPF hypoxia in lung tissues, higher level of IPF HIF-1α leads to chronic IPF even without further inflammatory stimulus. Fibrosis in Itself Leads to Fibrosis in IPF. This approach indicates that steroids, anti-inflammatory drugs are no longer clinically recommendable for the treatment of IPF.
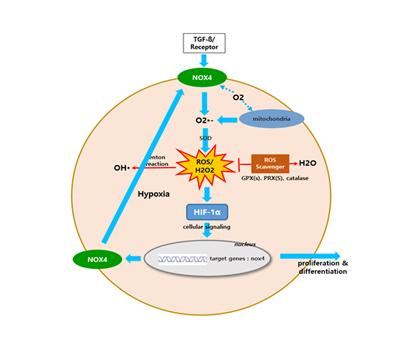
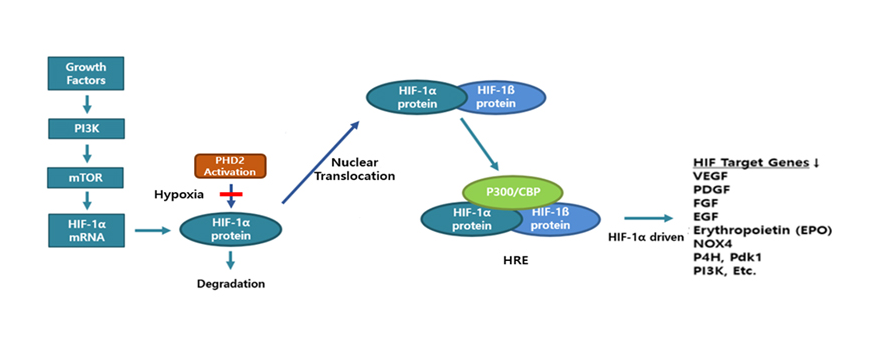
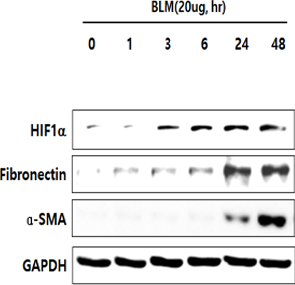
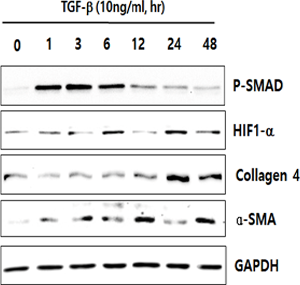
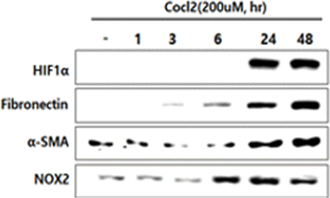
In human lung epithelial cells exposed to TGF-β, Bleomycin or CoCl2, increased expression of hypoxia-induced HIF-1α protein was observed, followed by increased fibrotic markers.
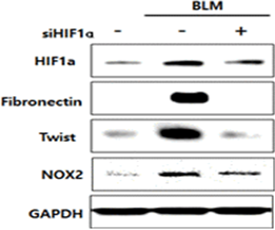
In human lung epithelial cells exposed to Bleomycin, forced reduction of HIF-1α via Antisense DNA leaded to decreased fibrotic markers.